Docker notes
Overview
What is it?
Docker is a platform/service that bundles and delivers software in containers.
Each container is a self-contained environment for the software to run.
Containers bundle the software and dependencies while isolating it from
the host environment. Containers are not VMs - they share the same host OS -
abstraction is at the app layer
Examples:
- Apache
- nginx
- mariadb
- your application
Why is it useful?
- Reproducable environment
- Easier deployment
- Pathway to scaling (eg Kubernetes)
Setup
- Make sure virtualization support is enabled in system BIOs
- Create an account on docker
Linux
Windows WSL2
- Download Docker for Windows
- In Docker for Windows settings enable WSL 2 based engine and
Enable integration with my default WSL distro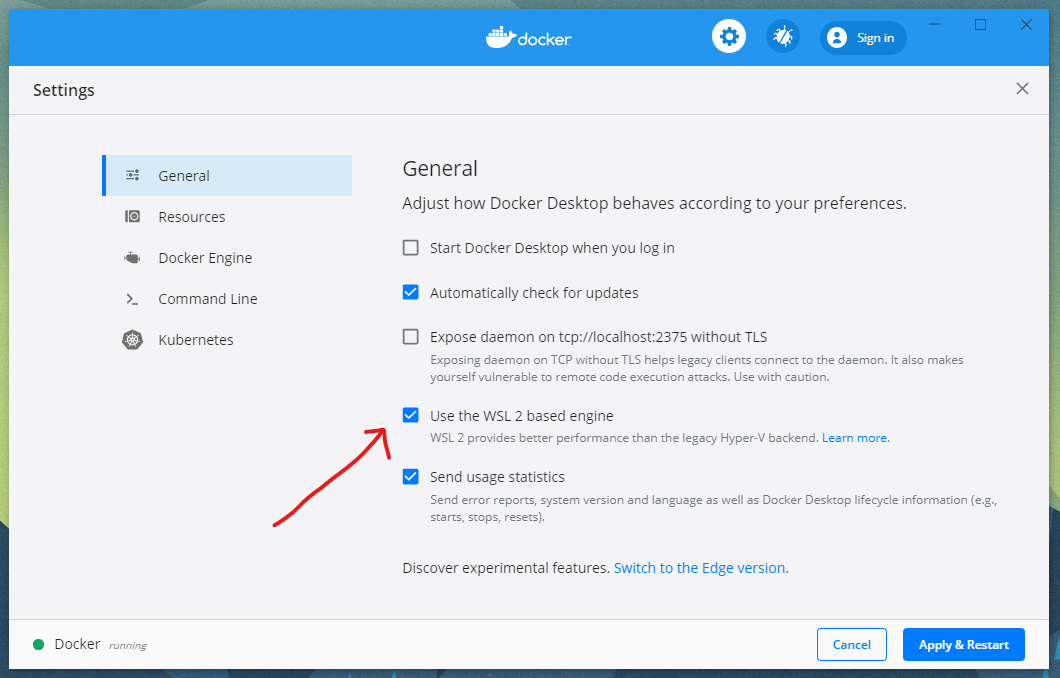
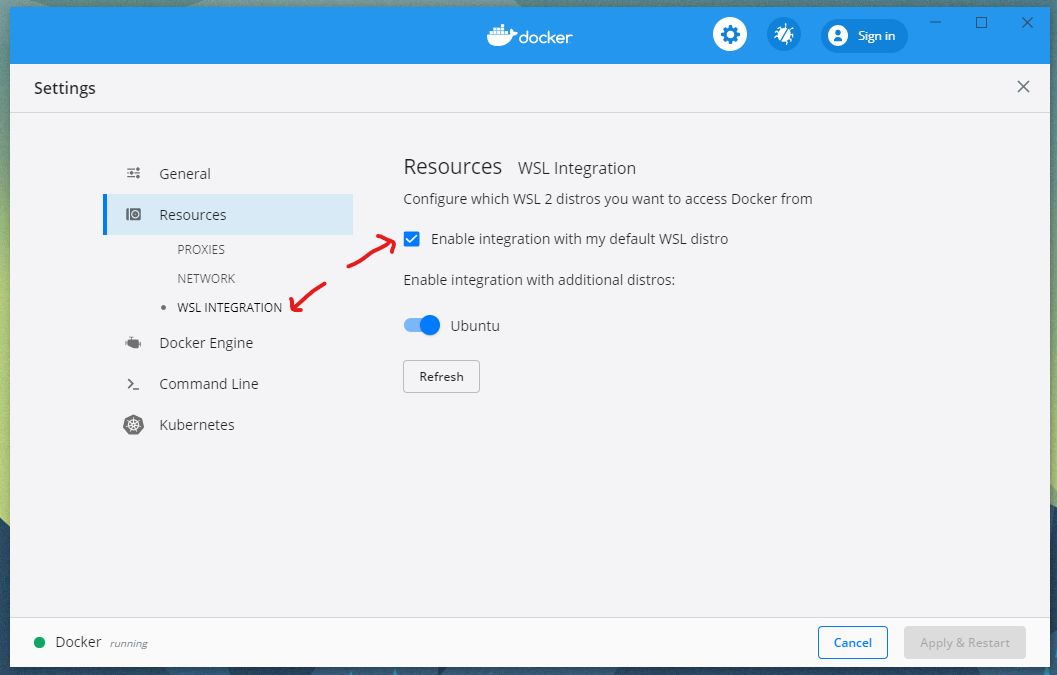
- Verify it is running with
docker info. Note, you may need to open a new WSL terminal if you started Docker with an existing terminal open.
Dockerfile
Dockerfiles are configuration files that allow you setup your conatiner. Docker has a repository of images for different applications. Dockerfiles let you specify a series of steps to perform on one of these images, allowing you to extend it (aka layer) and thus create a new image. For example, you might want to take an Ubuntu image add add a series of bash commands to apt-get install some additional packages.
Dockerfiles can do a variety of steps. Some examples:
- Set env variables (ENV)
- Run setup commands (RUN)
- Copy files from the host the container (COPY)
- Mount a host folder into the container (VOLUME)
- Map ports from the host machine to container (EXPOSE)
- Specify a command to run when started (CMD)
You can build and upload your custom images into the Docker repo.
Example
FROM nginx
COPY static-html-directory /usr/share/nginx/htmlSnippits
# Build the Dockerfile in the current folder
docker image build -t zeddic/test .
# Run the image
docker container run zeddic/test:latest
# Upload your image
docker login
docker push zeddic/testDocker Compose
docker-compose.yml is another configuration file that allows you to specify a series of containers that should be brought up together and how they should be linked.
For example, this could allow you to bring up an entire LAMP stack or a NodeJS/nginx/mongodb stack.
Example from the official docs:
version: '3'
services:
web:
build: .
ports:
- '5000:5000'
redis:
image: 'redis:alpine'This example creates an image for web by building from the Dockerfile in the current directory and exposes port 5000 on the container. It also will start up a redis image using the offical repo image.
# Starts all containers (in detached mode)
docker-compose up -d
docker-compose down
# Shuts down all containers. -v removes all anonymous volumes
docker-compose rm -v
# Recreate anonymous volumes instead of using those from last run
docker-compose up -V
# Force recration of containers
docker-compose up --force-recreateGists
# List all images
docker image ls
# List all containers
docker container ls
# Run a container in detached mode
docker container run -d nginx
# Shutdown a container
docker container rm $tag -f
# Open bash in one of the containers
docker-compose exec $containername bash